
Knowledge of the microbial flora of an environment and the sensitivity pattern are important tools in the management of wound infections especially those caused by Proteus species, and are also useful in formulating rational antibiotic policy. All the isolates were sensitive to ciprofoxacin, ofloxacin and gentamycin while all were resistant to tetracycline and erythromycin.
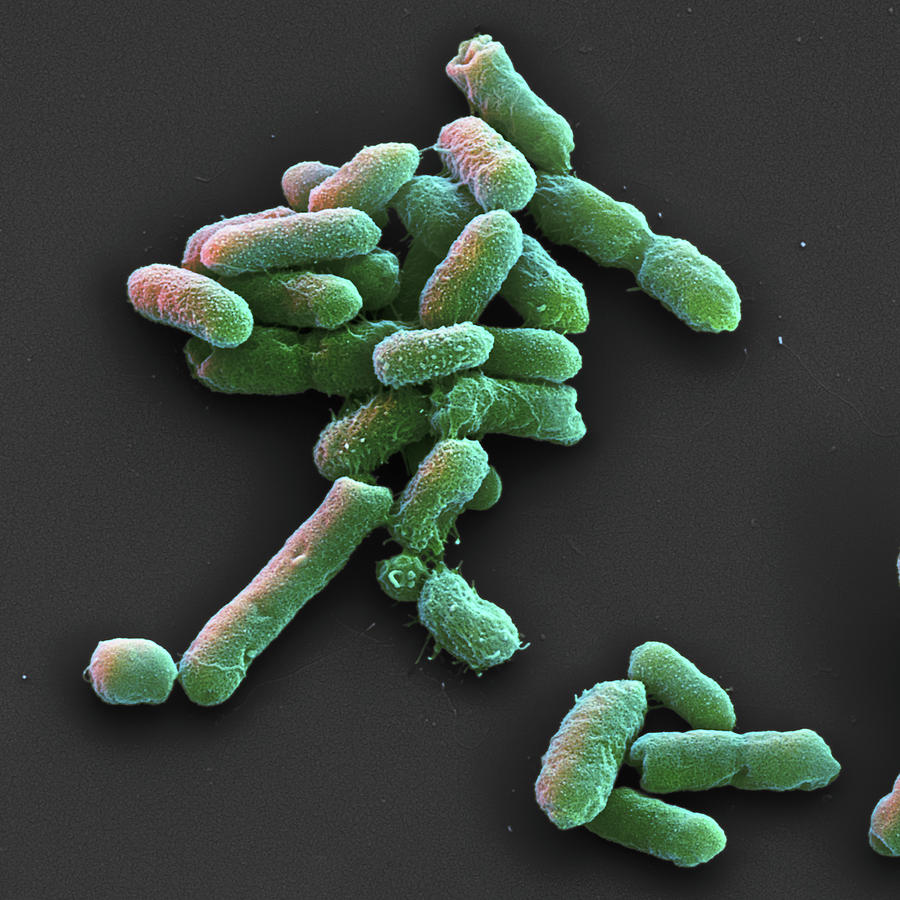

Proteus mirabilis was the Proteus species most commonly isolated, 97 (17.3%), Proteus vulgaris 40 (7.1%), Proteus rettgeri 8 (1.40%), and Proteus morgagni 5 (0.9%). Proteus species accounted for 150 (26.8%) of the isolates. Of the 400 wound samples from various parts of the body 390 (97.5%) yielded growths and produced 560 isolates. All isolates were tested for sensitivity against ciprofloxacin 5 µg, gentamycin 10 µg, streptomycin 10 µg, ofloxacin 5 mg/µg, chloramohenicol 10 µg, erythromycin 10 µg and tetracycline 10 µg. Monitor renal function and provide adequate. Switch from intravenous to oral therapy as soon as possible once directed based on identification and sensitivities. Replace only if required and only after patient has completely responded to therapy. Wound swabs and aspirates from various parts of the body and consisting of accidental, pathological and post-operative wounds were collected from patients who attended the clinics at the UBTH and examined by standard bacteriological methods. Repeat blood cultures, if positive, to document clearance. There was a distribution of Proteus species isolated from various wound infections. This was a prospective and cross-sectional study. Pathological wound infections were 160 samples with a total of 250 (44.64) isolates trauma wound swabs were 140 and yielded 185 (33.04) isolates post-operative wounds were 100 samples and yielded 125 (22.32) isolates. Anyone can become infected with Proteus species in the urinary tract or vagina, but some groups are more at risk than others. The study also determined the sensitivity pattern of the Proteus isolates. Proteus organisms are believed to be responsible for serious infections in humans, being most commonly found in the digestive tract, but also in the urinary tract. This study was carried out at the University of Benin Teaching Hospital (UBTH) to determine the involvement of Proteus species as one of the major causative organisms in wound infections. Proteus Infections is a descriptor in the National Library of Medicines controlled vocabulary thesaurus, MeSH (Medical Subject Headings). They contaminate wounds and thus cause infections. Proteus species are frequently recovered from infected wounds.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
